What is Mitochondrial DNA?
Mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) is a special type of DNA found in the mitochondria of your cells. These are tiny structures inside the cell that produce energy. Unlike most DNA, which is located in the cell’s nucleus, mitochondrial DNA is found outside the nucleus.
How is Mitochondrial DNA Inherited?
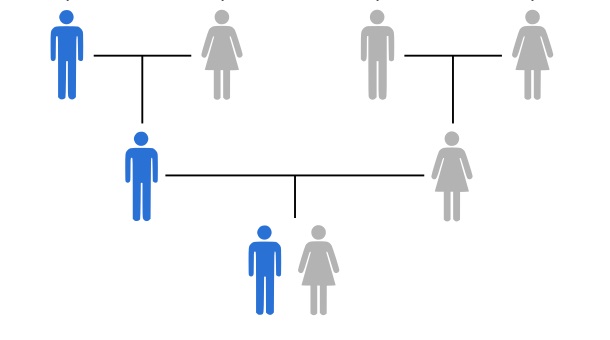
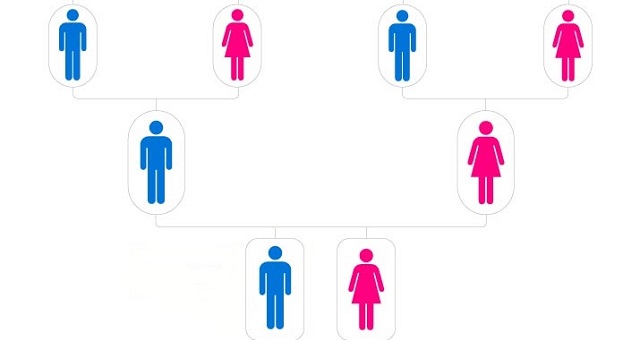
Mitochondrial DNA is inherited almost exclusively from your mother. When a baby is conceived, it receives its mitochondria (and thus its mitochondrial DNA) from the mother’s egg cell. This means that both boys and girls inherit their mitochondrial DNA from their mothers, but only daughters can pass it on to their children. This unique pattern of inheritance allows scientists to trace a person’s maternal lineage far back in time.
Tracing Maternal Ancestry
Mitochondrial DNA is used to trace your maternal ancestry because it is passed down from mother to child largely unchanged over many generations. By studying mtDNA, scientists can trace back your family tree on your mother’s side, even thousands of years.
Identifying Maternal Haplogroups
Mitochondrial DNA helps identify haplogroups, which are groups of people who share a common ancestor on their maternal line. These haplogroups are like branches on a family tree. By knowing your haplogroup, you can learn about your ancient ancestors and their migration patterns.
Understanding Human Evolution and Migration
Scientists use mitochondrial DNA to study human evolution and migration. By comparing mtDNA from people all over the world, they can map out how ancient humans moved and settled in different regions.
How is Mitochondrial DNA Tested?
To test mitochondrial DNA, a sample of your DNA is collected using a simple and painless cheek swab or saliva sample. The sample is then sent to a laboratory, where scientists analyze the mitochondrial DNA. They look at specific regions of the mtDNA to find genetic markers that can tell them about your maternal ancestry.
Mutations in Mitochondrial DNA
Even though mitochondrial DNA changes very slowly, it can still undergo small changes called mutations. These mutations are random changes in the DNA code that happen over time. Scientists use these mutations to estimate how long ago two people likely shared a common maternal ancestor. The more mutations there are, generally the longer it has been since a common ancestor was alive.
Summary
Mitochondrial DNA is a special type of DNA found in the mitochondria, inherited almost exclusively from your mother. It is used to trace your maternal ancestry, identify maternal haplogroups, and understand human evolution and migration.